What is adoption?
Adoption is the legal process of establishing a permanent parent-child relationship between individuals who are not biologically related. Once finalized, adoptive parents gain all the rights and responsibilities of raising the child, while the birth parents’ legal rights are terminated. Adoption can take place domestically, internationally, or through foster-to-adopt programs, and the process often involves extensive legal, emotional, and social considerations.
Data by AFCARS shows that for children in foster care one of the main case plan goals is reunification with parents or primary caretakers, and after that adoption. Those who are eligible for adoption wait, on average, two-three years and are mostly adopted by foster parents.
For more information see AFCARS report.
What is Surrogacy?
Surrogacy is a family-building option where a woman (the surrogate) carries a pregnancy for intended parents who cannot conceive or carry a child on their own. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate has no genetic link to the baby, as the embryo is created using IVF from the intended parents’ or donors’ eggs and sperm. Learn more about the surrogacy process and the full details of what surrogacy is.
- An increasing number of international intended parents are utilizing gestational surrogacy in the US. From 2014 (n = 2758, 22.0%) to 2019 (n = 4905, 39.8%) (Herweck 2024)
- Use of gestational carriers increased during 1999–2013. Between 1999 and 2013, there were 30,927 surrogate pregnancies in the U.S., yielding about 18,400 infants (including singletons and multiples). (Perkins et al. 2016)
- In 2020, gestational carrier (surrogate) cycles made up about 4.7% of all embryo transfer cycles — a rise from about 2.2% in 2011. Explore the statistics on Cato Institute.
What are the main differences between surrogacy and adoption?
The process (Matching and Legal process)
In adoption, the process begins with matching adoptive parents to a child or an expectant mother, and the legal steps involve terminating birth parents’ rights before the adoption can be finalized.
Surrogacy follows a more structured path, with both surrogate and intended parents undergoing screening, entering into a legal contract, and moving forward with medical procedures. In many cases, intended parents in surrogacy can establish parentage before the child is even born.
Genetics
A major difference between adoption and surrogacy is genetics. Adoptive parents typically do not share a biological link with their child, unless the adoption involves a relative. In surrogacy, however, one or both intended parents often share a genetic connection to the baby, which can be a significant factor for families who want that biological tie.
Surrogacy vs Adoption Cost in 2025
Adoption costs vary widely depending on whether the adoption is domestic, international, or through foster care, but generally range from $30,000 – $50,000.
Surrogacy costs are higher, averaging $100,000–$150,000, because they include medical expenses, surrogate compensation, and agency and legal fees. While adoption can be less expensive, surrogacy often provides more predictability and clarity in the process.
Wait Time
The wait time for adoption can be uncertain, sometimes lasting years depending on the program, the birth parents’ decisions, and legal complexities. Surrogacy, on the other hand, has a more predictable timeline. From the time intended parents are matched with a surrogate to the baby’s birth, the journey usually takes 15–24 months.
Contact
Another difference lies in the possibility of ongoing contact. In adoption, some families pursue open adoptions, where adoptive parents and biological parents maintain some level of communication throughout the child’s life. Others may choose closed adoptions with no ongoing contact. In surrogacy, intended parents typically build a relationship with their gestational carrier during the pregnancy, with ongoing updates, appointments, and shared milestones. After birth, the level of continued contact with the surrogate depends on mutual preference and the relationship built during the journey.
Surrogacy vs adoption in California
California is considered one of the most surrogacy-friendly states in the U.S. Intended parents benefit from clear laws that allow pre-birth parentage orders, ensuring their names are listed on the birth certificate immediately. Adoption in California, however, requires consent from birth parents, termination of parental rights, and a court process before finalization. For families in California, surrogacy offers more legal certainty and smoother parentage recognition compared to adoption.
Surrogacy Pros and Cons
Pros
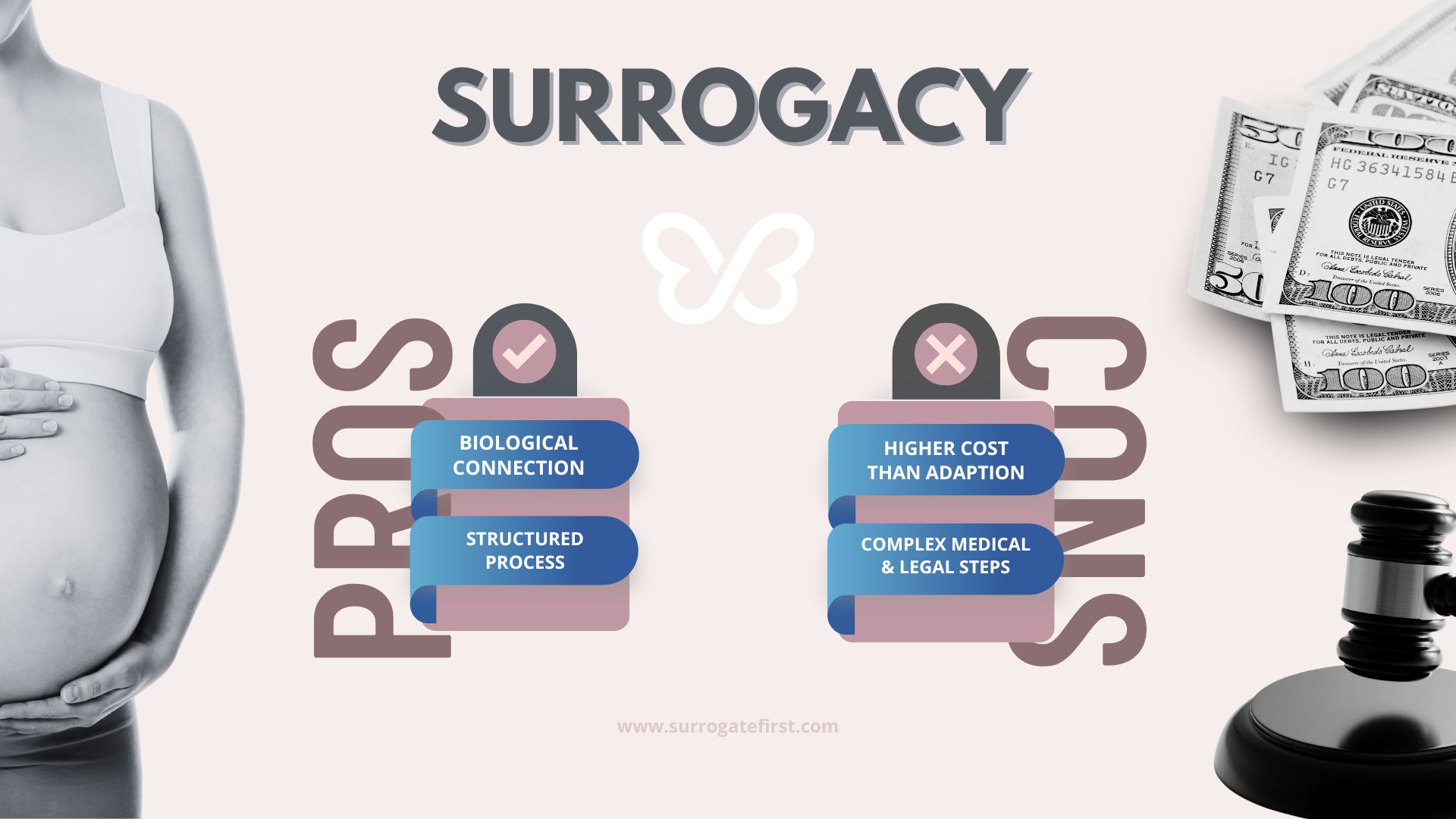
- Biological connection to the child. One of the biggest advantages of surrogacy is that it allows one or both intended parents to have a genetic link to their baby. For many families, this connection is deeply meaningful, giving them a sense of continuity and identity that adoption cannot provide.
- Structured and secure process. Surrogacy follows a carefully managed journey involving medical treatment, legal contracts, and agency support. These safeguards create a clear framework that helps intended parents feel more confident and reassured throughout the process.
Cons
- Higher financial cost. Surrogacy is significantly more expensive than adoption, with total costs often ranging from $100,000–$150,000. For some families, this financial commitment can be the single largest barrier to pursuing this path.
- Complex medical and legal requirements. The surrogacy journey involves IVF treatments, extensive screenings, and legal agreements. While these steps ensure protection for everyone involved, they can also feel overwhelming and emotionally demanding at times.
Adoption Pros and Cons
Pros
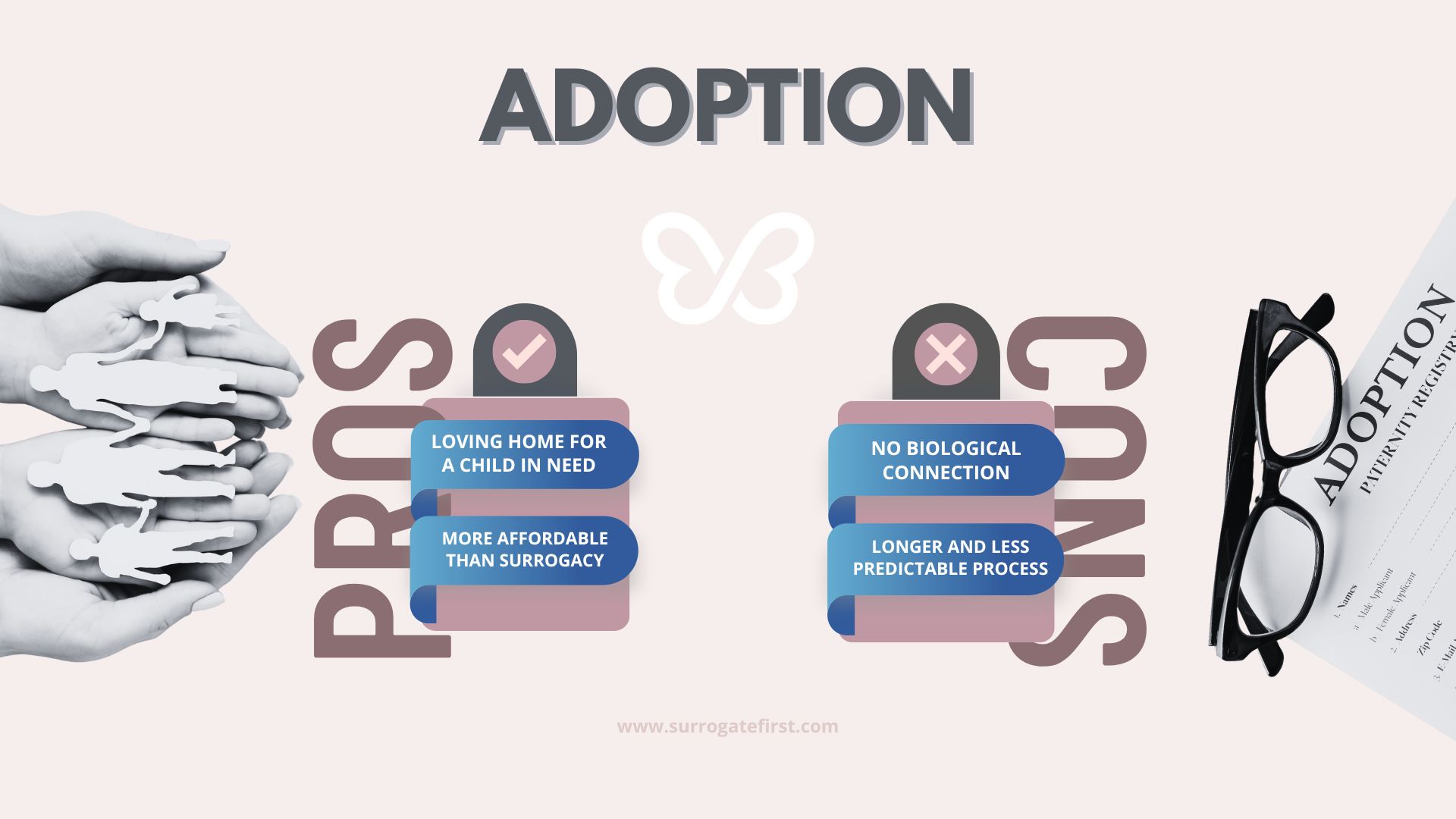
- Provides a loving home for a child in need. Adoption allows families to open their hearts and homes to children who may not otherwise have stable or permanent care, creating life-changing opportunities for both parent and child.
- More affordable than surrogacy. While costs vary by type of adoption, it is generally less expensive than pursuing surrogacy, making it a more accessible option for many families.
Cons
- No biological connection. Adoptive parents will not share a genetic link with their child, which can be a deciding factor for families who value biological ties.
- Longer and less predictable process. Adoption timelines often depend on birth parent decisions, legal procedures, and agency waitlists, which can result in lengthy and uncertain waiting periods.
SurrogateFirst: A Surrogacy Agency
At SurrogateFirst, we believe surrogacy is more than a process. It’s a partnership built on trust, compassion, and transparency. Our team supports intended parents and surrogates every step of the way, ensuring that the journey to parenthood is guided with care. If you are exploring whether surrogacy is the right path for your family, connect with us today.
Why SurrogateFirst?
At SurrogateFirst, we’re more than a matching agency—we’re your support system.
- Compassionate, personalized matching
- 24/7 access to dedicated case managers
- Legal and medical coordination
- Transparent pricing
- Emotional support for surrogates and for intended parents alike